Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Sugino, Hiroyuki; Suyama, Kenya; Okuno, Hiroshi
Proceedings of 8th International Conference on Nuclear Criticality Safety (ICNC 2007), p.144 - 150, 2007/05
Accurate calculation the isotopic composition of spent nuclear fuels (SNF) is important to evaluate the criticality safety of fuel cycle facilities. In the burnup calculation, the burnup value is traditionally used to obtain the exposure value of PIE samples. Because calculation codes and data libraries have been revised progressively, re-evaluation of the burnup values using the latest nuclear data library and calculation method is important to confirm quality of burnup analysis. Based on this idea, the burnup value of Obrigheim PIE data was re-examined to understand the level of the influence. This study shows that the maximum difference of 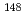 Nd calculation from experimental results is reduced from 1.0 % to 0.7 % by re-evaluation of the burnup value using latest nuclear data, and the deviation of neutron multiplication factor is approximately 0.5 %.
Nd calculation from experimental results is reduced from 1.0 % to 0.7 % by re-evaluation of the burnup value using latest nuclear data, and the deviation of neutron multiplication factor is approximately 0.5 %.
Okuno, Hiroshi; Suyama, Kenya; Okuda, Yasuhisa*; Yoshiyama, Hiroshi*; Miyoshi, Yoshinori
Proceedings of 8th International Conference on Nuclear Criticality Safety (ICNC 2007), p.140 - 143, 2007/05
In this research, a preliminary critical safe evaluation of a canister was performed, which stored either (1) four UO fuel assemblies (initial uranium enrichment of 4.1 wt%) or (2) four mixed uranium and plutonium oxide (MOX) fuel assemblies (initial plutonium enrichment of 10 wt%) for pressurized-water reactors (PWRs) in the earth for 1000 years without a crash of a fuel bundle. Ten actinide nuclides were chosen, most of which based on "A Guide Introducing Burnup Credit, Preliminary Version", and their compositions were computed with the SWAT code system. Criticality calculations were carried out with the MVP code adopting the computed composition, and the neutron multiplication factor was calculated to be less than 0.9. Issues for consideration were finally summarized.
fuel assemblies (initial uranium enrichment of 4.1 wt%) or (2) four mixed uranium and plutonium oxide (MOX) fuel assemblies (initial plutonium enrichment of 10 wt%) for pressurized-water reactors (PWRs) in the earth for 1000 years without a crash of a fuel bundle. Ten actinide nuclides were chosen, most of which based on "A Guide Introducing Burnup Credit, Preliminary Version", and their compositions were computed with the SWAT code system. Criticality calculations were carried out with the MVP code adopting the computed composition, and the neutron multiplication factor was calculated to be less than 0.9. Issues for consideration were finally summarized.
Shimizu, Yoshio; Suitsu, Yuichi; Murakami, Tatsutoshi; Yuri, Akiya
Proceedings of 8th International Conference on Nuclear Criticality Safety (ICNC 2007), p.335 - 340, 2007/05
Nuclear criticality safety evaluations for the fast breeder reactor's MOX fuel fabrication facility were performed. In the parametric studies made with SCALE, following three cases are here introduced. (1) The effect of the plutonium isotopic ratio on Pu (
( U,
U,  Pu,
Pu,  Pu) mass control were evaluated. The design conditions of the plutonium isotopic ratio under the operating condition were adjusted from the evaluation. (2) The moderation effects of organic materials in MOX fuel fabrication facility were evaluated. The water contents equivalent moderation effects to organic contents were obtained from the evaluation. (3) The effects of nonuniform mixture of MOX powder and water were evaluated by two-phase model and SMORES. The
Pu) mass control were evaluated. The design conditions of the plutonium isotopic ratio under the operating condition were adjusted from the evaluation. (2) The moderation effects of organic materials in MOX fuel fabrication facility were evaluated. The water contents equivalent moderation effects to organic contents were obtained from the evaluation. (3) The effects of nonuniform mixture of MOX powder and water were evaluated by two-phase model and SMORES. The  k, which differ from the k
k, which differ from the k of uniform model, were evaluated.
of uniform model, were evaluated.
Tonoike, Kotaro; Miyoshi, Yoshinori; Uchiyama, Gunzo; Watanabe, Shoichi*; Yamamoto, Toshihiro*
Proceedings of 8th International Conference on Nuclear Criticality Safety (ICNC 2007), p.222 - 227, 2007/05
In order to obtain systematic benchmark criticality data concerning dissolving process in a reprocessing plant for LWR spent fuel, a series of critical experiments were performed using heterogeneous cores at the Static Experiment Critical Facility (STACY) in Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA). Focusing on the introduction of the burn-up credit to the process, critical mass measurement was conducted for a combination of uranium fuel rods and uranium solution where pseudo fission product (FP) materials were doped. In this report, the "pseudo FP materials" means elements such as Sm, Cs, Rh and Eu whose isotopic composition is natural but which contains some FP nuclide(s). The result is going to provide basic experimental data for validation of computational methods to evaluate a reactivity effect of each FP material, as well as benchmark criticality data for validation of neutron multiplication factor calculation of heterogeneous systems of spent fuel. In the report, detail of the experiments including a differential reactivity worth curve over the solution level variation is going to be provided as well as the procedure and the result of separate reactivity worth evaluation of each pseudo FP material. Comparison of the experimental result and the computational evaluation will also be presented.
Yamane, Yuichi; Takahashi, Satoshi*; Yamamoto, Toshihiro*; Miyoshi, Yoshinori
no journal, ,
Some criticality accident scenarios for MOX powder system were made based on the information of Rokkasho plant. For the mixture of two types of MOX powders which enrichment were different from each other, it was shown that mixing of powders could give rise to 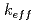 greater than 0.95 for the case with more then 13.6kg of zinc stearate. For such case, the progress of criticality accident was considered and divided into three cases, and a kinetics analysis was done for a typical condition in each case using several kinetics codes. The comparison of those results showed that total fission yield for MOX powder system is about 1 - 2
greater than 0.95 for the case with more then 13.6kg of zinc stearate. For such case, the progress of criticality accident was considered and divided into three cases, and a kinetics analysis was done for a typical condition in each case using several kinetics codes. The comparison of those results showed that total fission yield for MOX powder system is about 1 - 2 
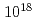 fission.
fission.